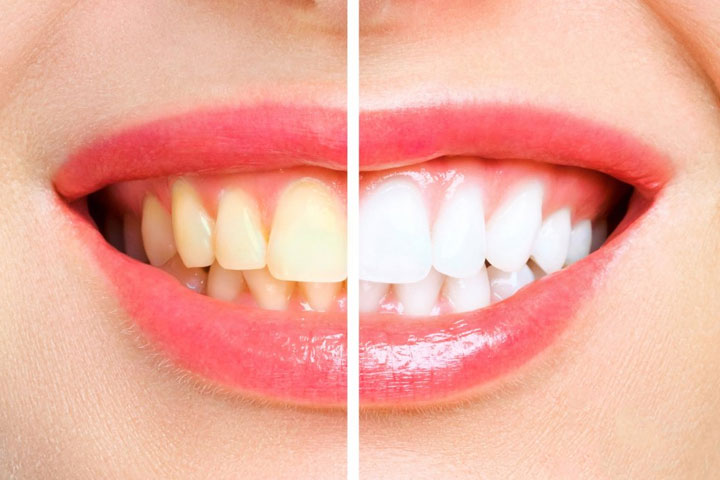
Brushing and flossing are everyday ways to keep your teeth bright, white, and healthy. Still, if you might feel like your smile is lacking some sparkle or is more yellow than it used to be, you’re not alone. When the American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry asked people what they’d most like to improve about their smile, the most common response was whiter teeth. The American Association of Orthodontists also found that nearly 90% of patients requested tooth whitening.
Thinking about teeth whitening? Get the facts first. Here are five of the most commonly asked questions about the process.
Over time, your teeth can go from white to not-so-bright for a number of reasons:
- Food and Drink Coffee, tea, and red wine are some major staining culprits. What do they have in common? Intense color pigments called chromogens that attach to the white, outer part of your tooth (enamel).
- Tobacco Use Two chemicals found in tobacco create stubborn stains: Tar and nicotine. Tar is naturally dark. Nicotine is colorless until it’s mixed with oxygen. Then, it turns into a yellowish, surface-staining substance.
- Age Below the hard, white outer shell of your teeth (enamel) is a softer area called dentin. Over time, the outer enamel layer gets thinner with brushing and more of the yellowish dentin shows through.
- Trauma If you’ve been hit in the mouth, your tooth may change color because it reacts to an injury by laying down more dentin, which is a darker layer under the enamel.
- Medications Tooth darkening can be a side effect of certain antihistamines, antipsychotics, and high blood pressure medications. Young children who are exposed to antibiotics like tetracycline and doxycycline when their teeth are forming (either in the womb or as a baby) may have discoloration of their adult teeth later in life. Chemotherapy and head and neck radiation can also darken teeth.
Types Of Bleaching (Tooth Whitening)
In-Office Bleaching
This procedure is called chairside bleaching and usually requires only one office visit. The dentist will apply either a protective gel to your gums or a rubber shield to protect your gums. Bleach is then applied to the teeth.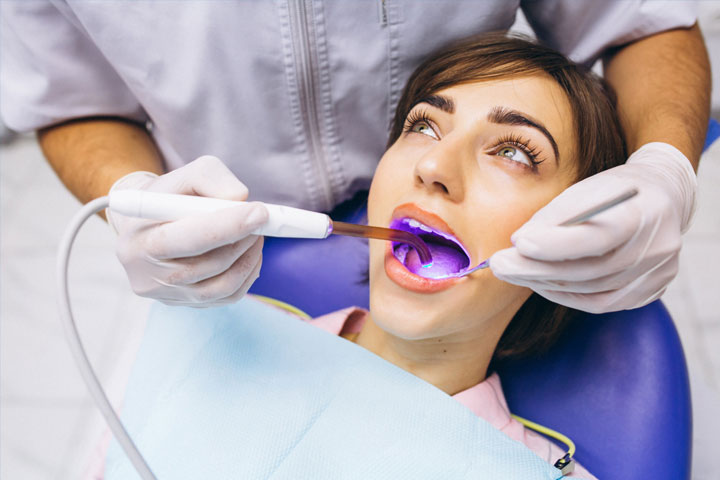
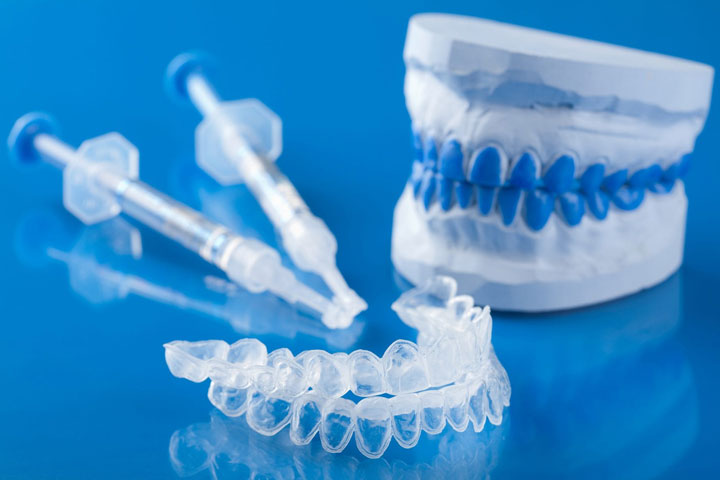
At-Home Bleaching from Your Dentist
Your dentist can provide you with a custom-made tray for at-home whitening. In this case, the dentist will give you instructions on how to place the bleaching solution in the tray and for what length of time. This may be a preferred option if you feel more comfortable whitening in your own home at a slower pace, but still with the guidance of a dentist. Out-of-office bleaching can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks.