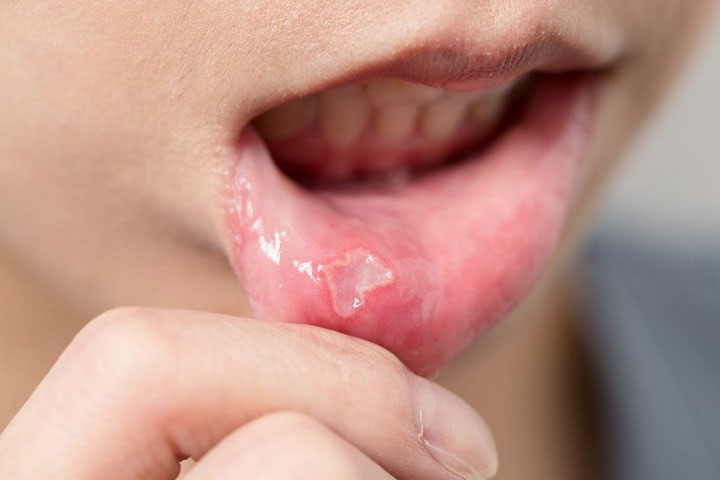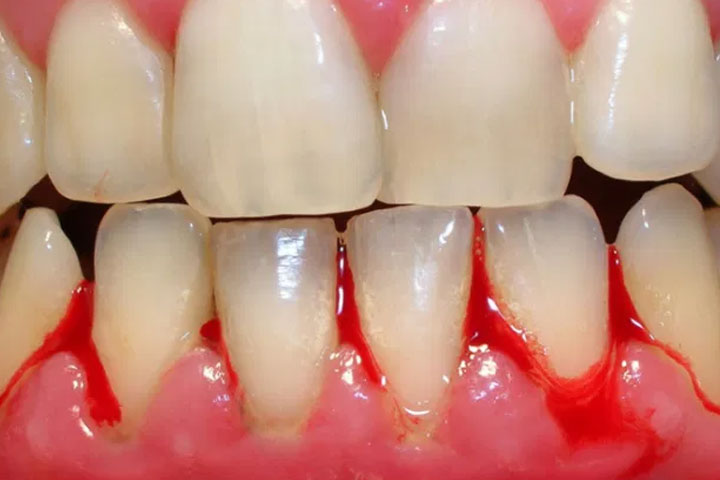
Bleeding gums is a serious problem. It indicates the beginning of the destructive process involving the supporting tissue around the tooth or some serious underlying systemic problems.
Causes of Bleeding Gums
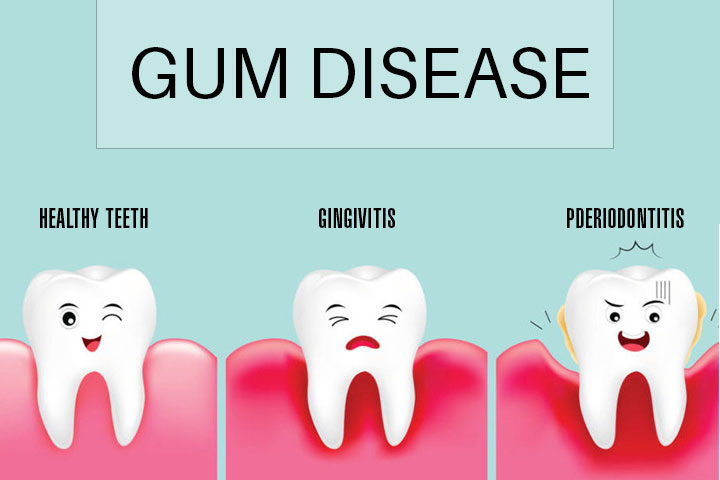
Plaque accumulation on teeth is the primary cause of poor gums. This plaque if not removed through regular brushing and dental appointments, will harden into what is known as tartar. Ultimately, this will lead to inflamed gums, a condition called gingivitis, increased bleeding, and finally a more advanced form of gum and jawbone disease known as periodontitis.
Other causes of bleeding gums include :
- Brushing too hard
- Improper flossing
- Infection, which can be either tooth or gum-related
- Scurvy (Vitamin C deficiency)
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy
- Leukemia (Blood Cancer)
- Ill-fitting dentures
- Use of blood thinners
- Maintain an unbalanced, unhealthy diet.
Tips to prevent bleeding
- Avoid the use of tobacco, which aggravates bleeding gums.
- Have poorly fitting dentures adjusted and relined by your dentist if they are causing sore spots in gums.
- Avoid aspirin unless your physician has recommended that you take it.
- Control gum bleeding by applying pressure directly on the gums with a gauze pad soaked in ice water.
- If you have been diagnosed with a vitamin deficiency, take recommended vitamin supplements.
- If the side effects of the medication are irritating, ask your doctor to adjust or substitute another medication. Never change your medication without consulting your doctor.
You should see your dentist if
- Your gums continue to bleed even after treatment
- The bleeding is severe or chronic
- Other unexplained symptoms are associated with bleeding.